
![]()
Column
03/2025
Fluoro Materials:
Catalysts for Medical Device Evolution
Realizing the Potential and Impact of Essential Fluoro Materials in Modern Healthcare
Fluoro Materials Driving Medical Device Innovation
Medical devices are an essential component in contemporary medicine, employed for screening, diagnosing and treating diseases. Possessing a more straightforward regulatory pathway to market, and enjoying wider accessibility, the medical device market is projected to grow rapidly both in procedure volume and new applications. These devices significantly enhance patients' quality of life, and fluoro materials play a pivotal role in their development.
1. The Critical Role of Medical Device Development
Current drivers in medical device development include the need for ever smaller devices, improved functionality/capability, surgical robotics, and real-time surgical guidance, possibly with artificial intelligence assists. Smaller devices can access the farther reaches of the anatomy without additional trauma. They are generally introduced through smaller access channels, promoting more rapid healing and reducing the possibility for hospital-acquired infection, a critical consideration given the rise in incidence of multiply-resistant bacterial infections.
Adding imaging and sensing modalities to catheters and endoscopes give the physician a real-time cut-don’t-cut decision making capability, enhancing the precision of surgery and accuracy of biopsy sampling. Flexible surgical robotics are now allowing the most difficult disease states to be properly diagnosed and treated. Lung cancer diagnosis and treatment for example is currently in a state of rapid and beneficial change as new flexible robotic bronchoscopes with image guided biopsy needles are being introduced. Because these can go through the trachea to the site of the tumors (natural orifice insertion), the need for incisions is removed which has dramatically improved patients' recovery times and minimized hospital stays.
Cardiovascular interventions are enjoying a similar renaissance with improved materials now allowing more procedures to be done with a radial approach. This reduces the need for a femoral artery incision and the associated healing complications from puncturing this critical high-pressure, high flow vessel. Finally, there is a new emphasis to employ one-time-use, pre-sterilized devices as opposed to reprocessing durable devices. This is also driven by the rise in prevalence of multiply-resistant strains of bacteria and their apparent immunity to standard hospital sterilization procedures.
2. Unique Properties and Applications of Fluoro Materials in Medical Devices
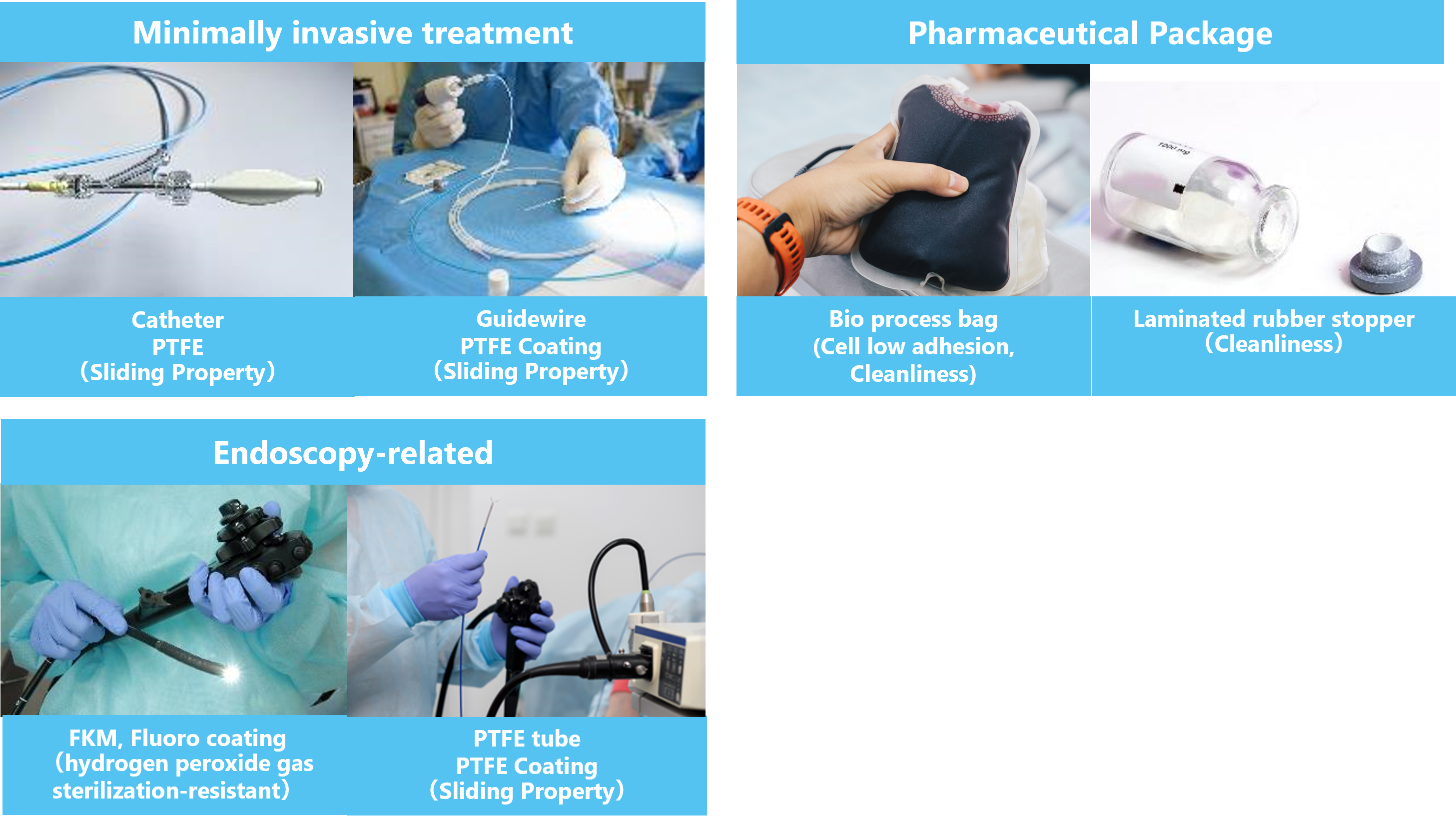
Fluoro materials are renowned for their exceptionally low coefficients of friction, chemical stability, cleanliness, and biocompatibility, making them critical in a myriad of medical device applications. (*1)
1) Low friction
The drive towards smaller crossing profiles for catheters, flexible robotics and endoscopes has in turn reduced the size of the working channels in these devices, the contiguous lumens through which guide wires, biopsy needles and other tools can be deployed. It is therefore critical that the inner lumens of these working channels, and the outer surfaces of the tools used be coated with materials with extremely low coefficients of friction so that the devices do not get bound up. PTFE, known for its ultra-low coefficient of friction, is extensively used as a coating material for catheter liner tubes and guidewires.
2) Unmatched Cleanliness
Fluoropolymers are free from plasticizers and exhibit high chemical stability. Its excellent non-adhesion properties make it ideal for packaging materials such as medicine bags and laminated rubber stoppers for vial bottles. Additionally, its superior low-temperature resistance is critical for cryopreservation containers storing cells and tissues.
3) Superior Chemical Resistance
Fluoro materials exhibit outstanding resistance to various solvents, acids, and bases. Fluorine rubber is expected to be used as a sealing material for equipment exposed to corrosive dialysis and disinfectant solutions, while Fluoro coatings protect reusable medical devices such as endoscopes, increasing durability and resistance to hydrogen peroxide gas sterilization.
Figure 1. Applications of Fluoro Materials in Medical Devices
3. Commitment to a Reliable Supply Chain
Fluoro materials are indispensable for medical devices that are needed to save and improve lives. And a stable supply of materials is required to ensure supplies of approved medical devices for patients since changes to medical devices take an extremely long time from development to commercialization or product availability. Specification & material changes after regulatory approval to ensure safety and efficacy with patients, are time consuming, require additional investment, and challenging.
As a global leader in fluorochemicals, our company consistently provides reliable quality products, minimizing environmental impact through sustainable production practices. Additionaly, we invest continuously in research and development of fluoro materials to meet various market requirements worldwide.
4. Meeting Future Medical Device Trends and Needs
Our company offers fluoropolymers with superior formability to meet these evolving market needs. We are also developing innovative catheter materials, including composite tubes (Fig. 2) where fluoropolymer and polyamide are directly bonded, and novel tubes (Fig. 3) where fluoropolymer is dispersed in PEEK resin, offering flexibility, strength, and sliding properties.
1) Coextruded EFEP-PEBA Tubing for Catheters
- The EFEP inner layer (liner) has as low coefficient of friction, which makes it easier for devices such as stents, balloons, and wires to pass through the tight confines of the inner catheter lumen.
- The PEBA “strike layer” creates a strong thermal bond between the EFEP inner layer and the outer Catheter jacket material.
- - EFEP (RP-5101) meet USP Class VI requirements.
Figure 2. Coextruded EFEP-PEBA Tubing for Catheters

Features o of EFEP-PEBA Co-Extrusion:
- Chemical resistance
- - Inner layer lubricity
- - Bondable outer layer
- - Biocompatability
- - Flexibility
Benefits of EFEP-PEBA Co-Extrusion:
- - Eliminates etching
- - Creates a strong chemical bond between EFEP-PEBA
- - Reduces labor and complexity of composite catheter construction
- - Increases reliability and quality
- - Increases productivity
- - Reduces delamination
2) Tubes Using PEEK/Fluoropolymer Composite Products
- - PEEK/Fluoropolymer composites (under development) combine the characteristics of PEEK and fluoropolymer, offering mechanical strength, heat resistance, biocompatibility, flexibility, and sliding properties.
-
- - It also has improved wear resistance compared to fluoropolymer, enhancing durability against guidewires and cleaning brushes inside endoscope lumen tubes.
Figure 3. Tubes Using PEEK/Fluoropolymer Composite Products
Features of PEEK/F composite tube:
- - Balance of flexibility and strength
- - Strong bending properties and cracking durability
- - Lubricity
Benefits of PEEK/F composite tube:
- - Improve the cracking and hardness of PEEK tubes
- - Enhance abrasion resistance to fluoro-tubes
Daikin continues to collaborate with customers to develop new products that cater to emerging medical device needs, leveraging our technological expertise that has produced over 2,000 fluorochemical products.
Contact us if you have questions on our portfolio of fluoro materials or need technical support.
(*1) Note: These products are designed for general industry use and the suitability or safety of medical equipment is not guaranteed.


